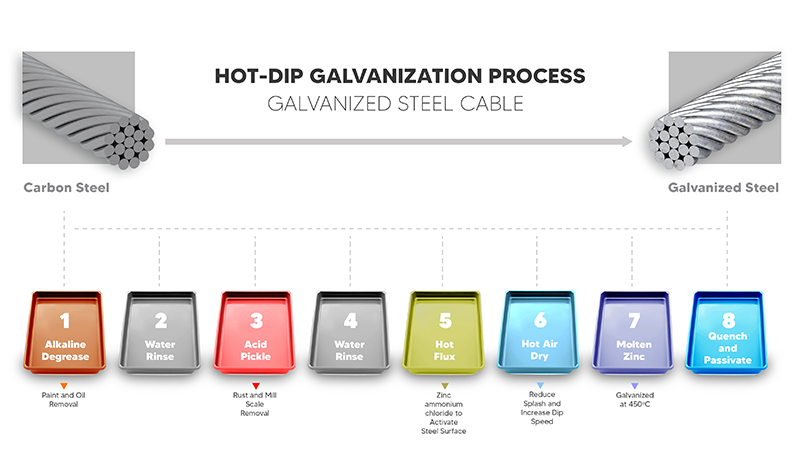
Galvanized steel is produced by coating carbon steel with a protective layer of zinc. To form galvanized wire rope, carbon steel wires are immersed in molten zinc and then cooled, forming galvanized steel wire. The newly formed galvanized steel wire is then fed into a stranding machine, where it is helically stranded to produce galvanized steel wire rope. Due to its excellent breaking strength, durability, and relatively low cost compared to its stainless steel counterpart, galvanized wire rope is a common choice in construction, agriculture, and manufacturing industries. To characterize galvanized steel wire rope's break strength, let's look at Sava's 3375 cable. With a diameter of 3/8 inches, it boasts a breaking strength of 14,400 lbs. Galvanized steel's durability is thanks to its aforementioned zinc coating. This coating acts as a barrier, protecting galvanized steel's vulnerable carbon core from wear and tear, moisture, and other corrosive elements that are often present in the final application's environment. While galvanized steel is water-resistant, it can corrode in saltwater due to chloride ion reactions. This reaction causes the coating to erode, thus exposing the underlying carbon steel. Stainless steel, which is naturally resistant to corrosion due to its lower carbon content, offers greater resistance to saltwater. However, due to its chemical makeup and a less demanding manufacturing process, galvanized steel is more cost-effective than stainless steel, making it more suitable for applications where harmful environmental factors are limited. Manufacturing galvanized steel begins with selecting the appropriate steel substrate, either high-carbon steel or low-carbon steel. The chemical composition of the steel is key as it affects the zinc coating's effectiveness. The zinc coating itself is applied primarily through three methods: hot-dip galvanizing, electrogalvanizing, or mechanical galvanizing. Finally, after coating, the steel wires are helically stranded into unique wire rope constructions. We've mentioned that galvanized steel is produced by coating carbon steel with a protective layer of zinc. However, there are many varieties of carbon steel, including high-carbon steel and low-carbon steel, and the selection of the carbon steel influences the galvanized steel result. High-carbon steel is defined as steel with a carbon content of 0.6-1.0%, while low-carbon steel, which contains up to 0.25-0.3% carbon. Galvanized steel generally consists of low-carbon steel as the substrate, due to its better formability and ease of coating with zinc compared to high-carbon steel. In addition to selecting the low-carbon steel, the chemical composition of the carbon steel must be considered to properly apply zinc coating. Composition of Carbon Steel to be Galvanized The zinc coating's primary function is to protect the carbon steel core from oxidation and other environmental damage. However, it's important to consider potential hydrogen embrittlement in high-strength steel, which can occur if the galvanization process is not carefully controlled. This can reduce the ductility and load-bearing capacity of the wire rope, highlighting the need for precise manufacturing practices. Hot-Dip Galvanizing  Electrogalvanizing  The Electrogalvanizing Process Mechanical Galvanizing  Zinc-Plated Steel Cable Eyelets 1. Wire Drawing The manufacturing process of galvanized steel wire rope begins with wire drawing. Steel billets are transformed into thin wires by pulling them through a series of dies. This process reduces the size of the wire to the diameter determined by the end result wire rope. 2. Galvanization Process Following the wire drawing, the next step is galvanization. As described earlier in the article, the drawn steel wires are immersed in a bath of molten zinc, ensuring a continuous zinc coating. 3. Stranding Techniques Various stranding configurations are employed to create wire rope, each offering distinct benefits: 1x19 Galvanized Wire Rope Trust 50+ Years of Manufacturing Experience An optional manufacturing step we have yet to mention is applying a natural plastic coating to the finished galvanized steel wire rope. Coatings such as FEP, nylon, and vinyl, each with their unique trade-offs, provide an additional barrier for galvanized steel wire rope. These plastic coatings enhance the cable's resistance to abrasion, chemical attack, and fatigue, making it more durable in demanding applications. For example, orange vinyl-coated galvanized steel wire ropes are often used as pull cords for operating safety switches that stop machines in emergencies. Galvanized wire rope is commonly used in suspension bridges, enduring constant exposure to rain, UV light, and wind. The zinc coating protects the steel core from corrosion, ensuring long-term durability and safety while under outdoor conditions. The characteristics of galvanized wire rope are ideal for elevators and lifting mechanisms. Its high breaking strength and excellent strength-to-weight ratio support the safe lifting of heavy loads, providing consistent performance in vertical transportation systems. This reliability is vital for safety and efficiency in applications where lifting and lowering heavy objects are routine. The first misconception is that galvanized steel cannot rust. While the zinc coating provides corrosion resistance to the carbon steel core, it is not invcincible to oxidation. Over time, corrosive factors can damage the zinc coating, exposing the carbon steel core which leads to potential rust. Another misconception is that all galvanized wire rope is the same. Various factors, such as coating thickness and wire rope construction, significantly influence the suitability for specific applications. Understanding these nuances helps in choosing the right galvanized wire rope for each unique application. Still have a few questions? We recommend talking to our cable experts®. This is the surest way to determine the material best suited to your project. For over 50 years now, Sava has been producing the galvanized wire rope the whole world uses. A measuring instrument for quantitatively evaluating the cylindricity of a cylinder by measuring the actual contour of the cylinder using the precise rotation centerline as the reference standard and the precise linear motion guide rail as the reference standard. It can be used to measure cylindrical shape errors (roundness, cylindricity, straightness, and flatness), position errors (coaxiality and verticality), etc. The cylindrical Roundness Tester is mainly used to measure the roundness, cylindricity, straightness, concentricity, coaxiality, flatness, parallelism, perpendicularity, surface waviness, discontinuous surface, etc. of various regular and irregular circular workpieces. It can also perform spectrum analysis, wave height analysis, eccentricity, shaft bending analysis, and runout analysis on workpieces. This device has excellent cost-effectiveness, full measurement capability, and is easy to learn and use. Cylindrical Measuring Instrument,Cylindricity Measuring Instrument ,3D Image Measuring Instrument,Roundness Measurement Instrument Zhejiang dexun instrument technology co., ltd , https://www.dexunmeasuring.com

How Galvanized Steel Wire Rope is Made
The Chemical Composition of Galvanized Steel
Source: Metalplate
Element
Composition
Carbon
Less than 0.25%
Phosphorus
Less than 0.05%
Manganese
Less than 1.3%
Silicon
0–0.04% or 0.15–0.25%
Zinc Coating Properties
Methods of Galvanization

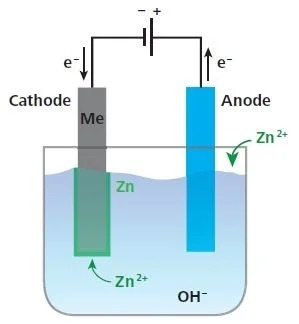

•
Electrogalvanizing in an alkaline zinc bath


•
Carl Stahl Sava IndustriesStranding Galvanized Steel Wire Rope in Three Steps


•
Carl Stahl Sava IndustriesShop Sava's Galvanized Steel Wire Rope
Cable Coatings for Galvanized Wire Rope


Galvanized Wire Rope: Common Applications
Suspension Bridges
Lifting Mechanisms
Galvanized Wire Rope: Common Misconceptions

Shop Now
July 24, 2024